Product is something that satisfies a Business Need. Product delivers value to the stakeholders (internal or external). Product has a clear boundary, customers and achieves some measurable value.
A tangible product is a physical object that can be perceived by touch such as a building, vehicle, gadget, or clothing. An intangible product is a product that can only be perceived indirectly such as an insurance policy.
Types of Products
Broadly these are few different types of products
- Consumer Products : Products which satisfies the needs of an end customer
- A Shoe
- A Shirt
- A Watch

- Business Products : Products which satisfies the needs of internal customers (generally called Businesses)
- HR Management system for employees who manufacture the Shoes
- ERP system for managing the supply chain of shirts raw material and finished products
- CRM system for managing the leads and prospects for the watch

- Services as a Product : A product could be a service.
- For an IT company like TCS, Infosys, Wipro, IBM – providing human capacity could be a product
- For a Pest Control company providing Pest Control services could be a product
- For a car servicing company – providing services such as oil change, shampooing of the carpet of the car etc could be a product
Sub-Products
Sometimes a main product could have sub products.
- For Example MS Office is the main product. MS Office contains sub-Products such as MS Excel, MS Powerpoint, MS Word and so on.

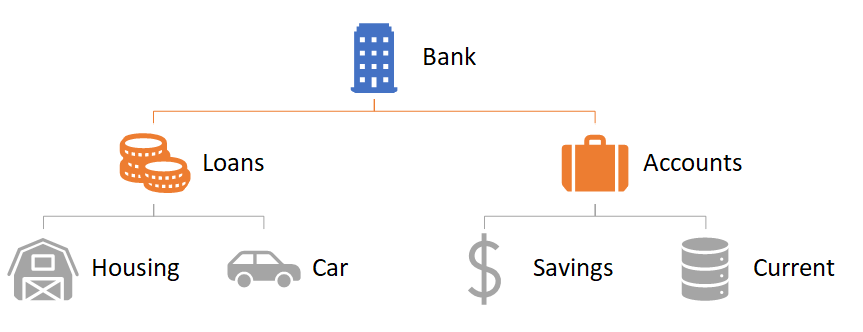
- In a Bank, there could be sub products such as accounts, mortgages and so on
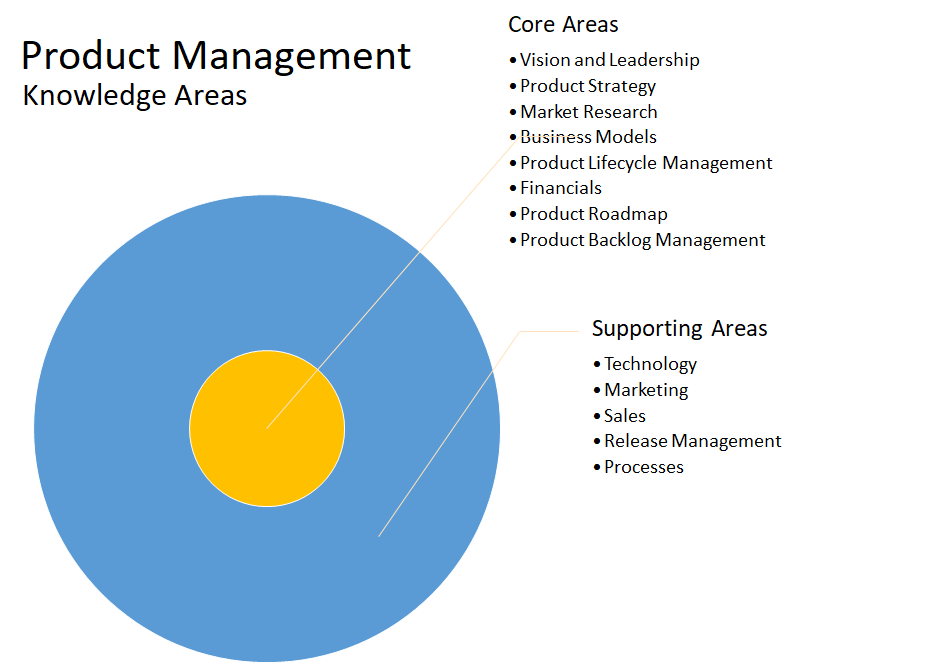
Product Management
Product management is an organizational lifecycle function within a company dealing with the planning, forecasting, and production, or marketing of a product or products at all stages of the product lifecycle. Similarly, product lifecycle management integrates people, data, processes and business systems. It provides product information for companies and their extended supply chain enterprise. The Product Management framework presented by Roman Pichler encapsulates all areas of Product Management pretty well
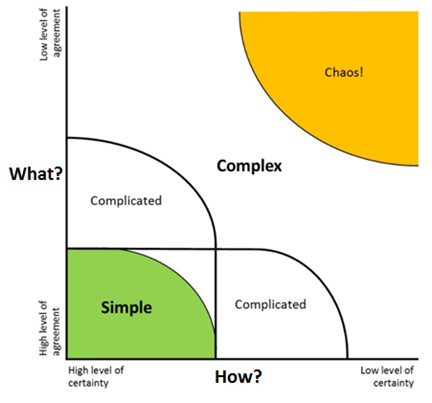
Why is Scrum Suitable for Product Development?
- When Product is built, product has a lot of unknowns/uncertainties. The unknowns are because of the unknown behavior of markets (consumers, users, end users etc). These unknowns are either on requirements or on technology. Therefore the best approach for a Product Owner is to get an hypothesis together about what the market “may” need. Then check the hypothesis by releasing products more frequently and testing the hypothesis. Product development work therefore is on the complex spectrum in the following diagram (courtesy Ralph Stacey Model)
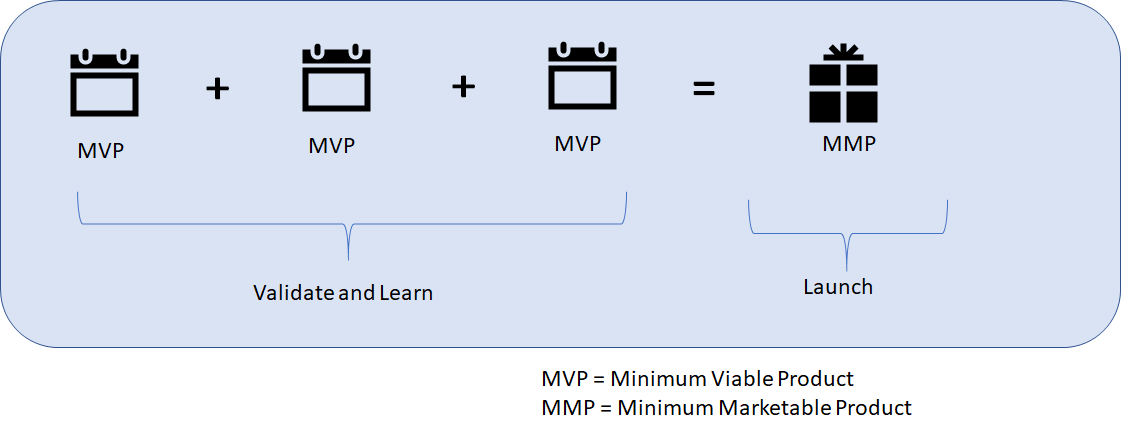
Scrum is an incremental and Iterative framework. That means Scrum requires the work to be broken down into small pieces and feedback is sought on it from stakeholders. Scrum builds small product increments (MVPs) and feedback is sought on it. Finally a Marketable product is developed which is the release candidate.
- Since Scrum works on Incremental+Iterative agile concept and is suitable for complex products, Scrum is suitable for product development which inherently has a lot of complexities.
- However, there may be products which are Simple or Complicated in nature where they can be built as set of known steps. Scrum may not be required for such products and traditional waterfall may also work. e.g. regulatory work, migration work etc
Conclusion
Product is something that satisfies business need. Product Management is an organizational lifecycle function which involves the end-to-end functions starting from envisioning to release of product to servicing of the products. Scrum is a framework meant for complex adaptive work. Product work is inherently complex work. Hence Scrum works beautifully for Product Management.
Some of the following blog posts may help with further understanding of this topic
